Cardiovascular System Cardiac Action Potential
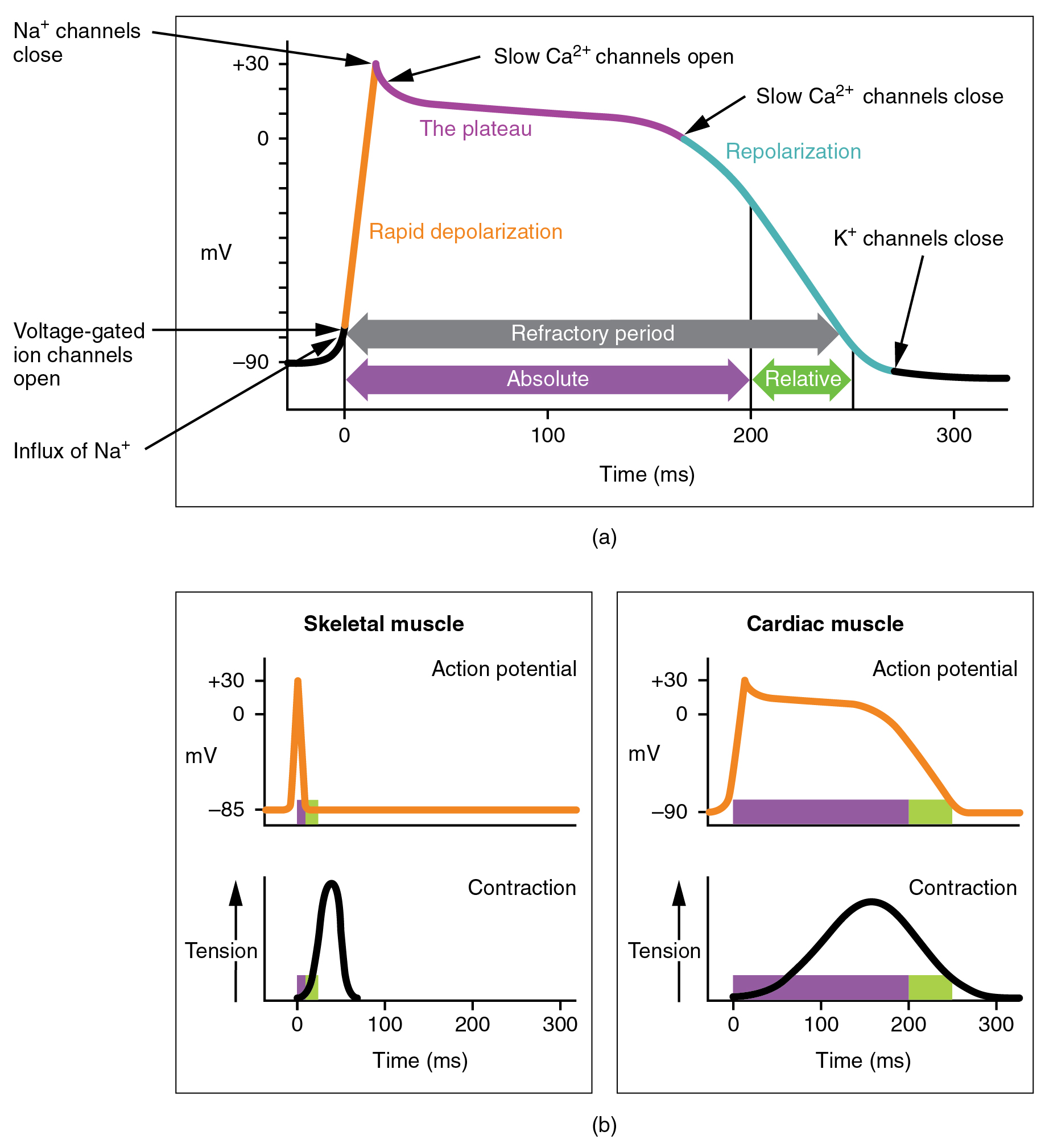
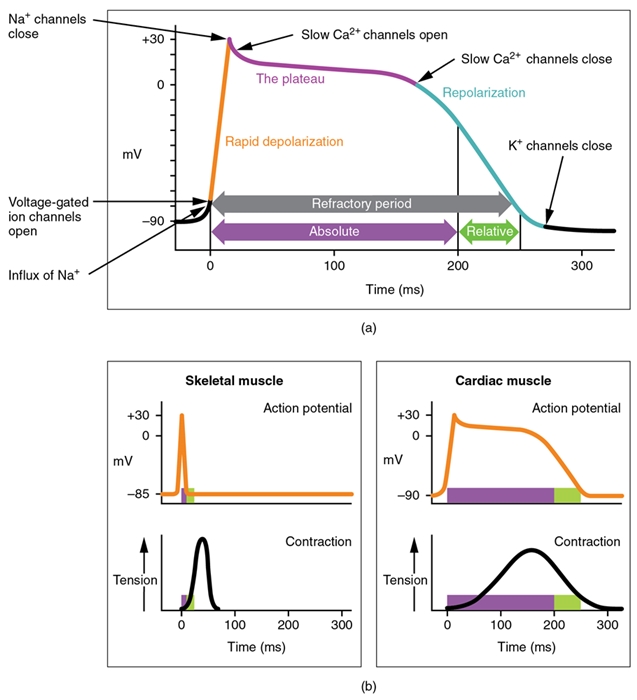
Cardiovascular system cardiac action potential. The basic function of the heart is to pump blood through the blood vessels. It is caused by a sudden increase in sodium inflow. Cardiac action potentials differ from the APs found in other areas of the body.
At the peak of action potential the membrane potential approaches the sodium equilibrium potential. Cardiac action potential with free interactive flashcards. Nervous and muscle cells as well as non-pacemaker cardiac cells use the opening of Na channels to facilitate the depolarisation phase whereas cardiac pacemaker cells.
The cardiac action potential describes the molecular basis of electrical activity within the hearts cardiomyocytes. Pulmonary lungs systemic the rest of the body responsible for the flow of blood nutrients oxygen and other gases and hormones to and from cells about 2000 gallons 7572 liters of blood. We consider here the action potential of SA nodal cells and ventricular muscle cells.
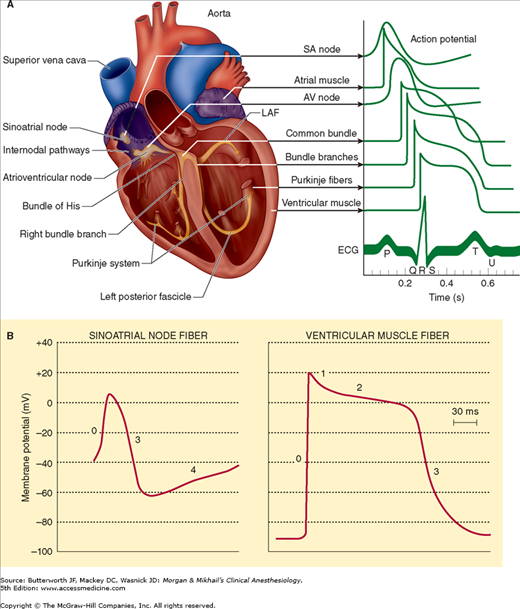
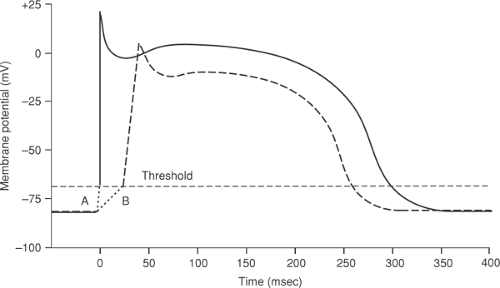
The cardiovascular system is composed of the heart and blood vessels. Cardiac cycle and the JVP waves. The cardiac action potential takes a different form in different cardiac cells which include SA nodal cells atrial muscle cells AV nodal cells Purkinje fibers and ventricular muscle cells.
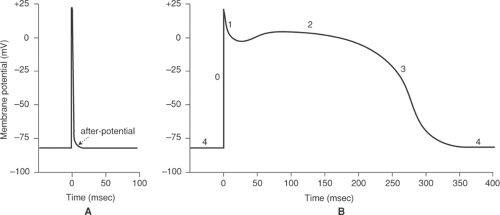
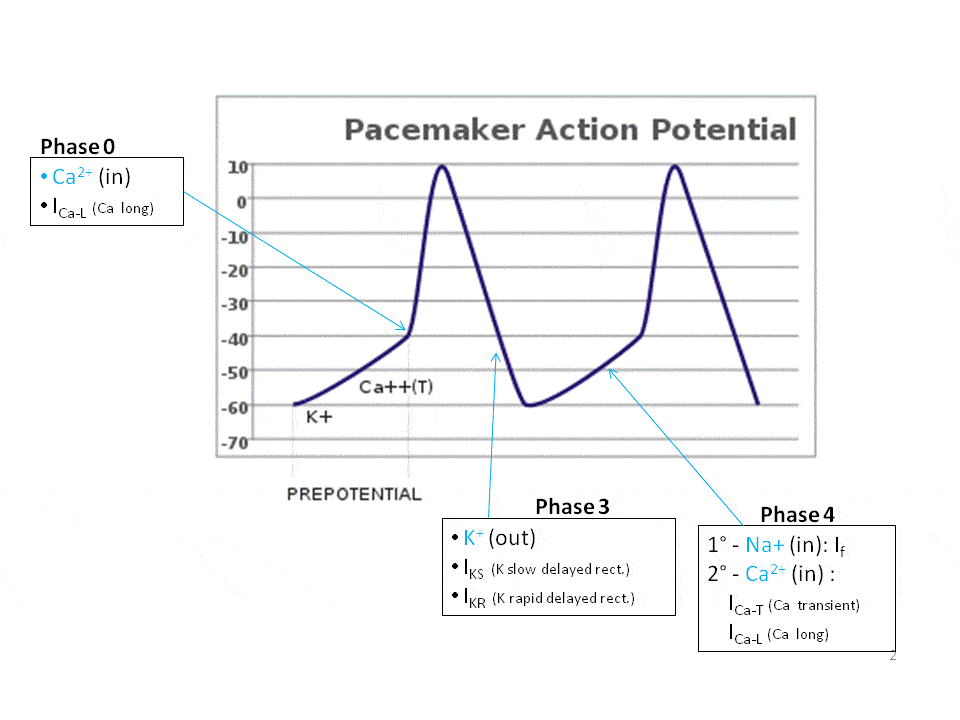
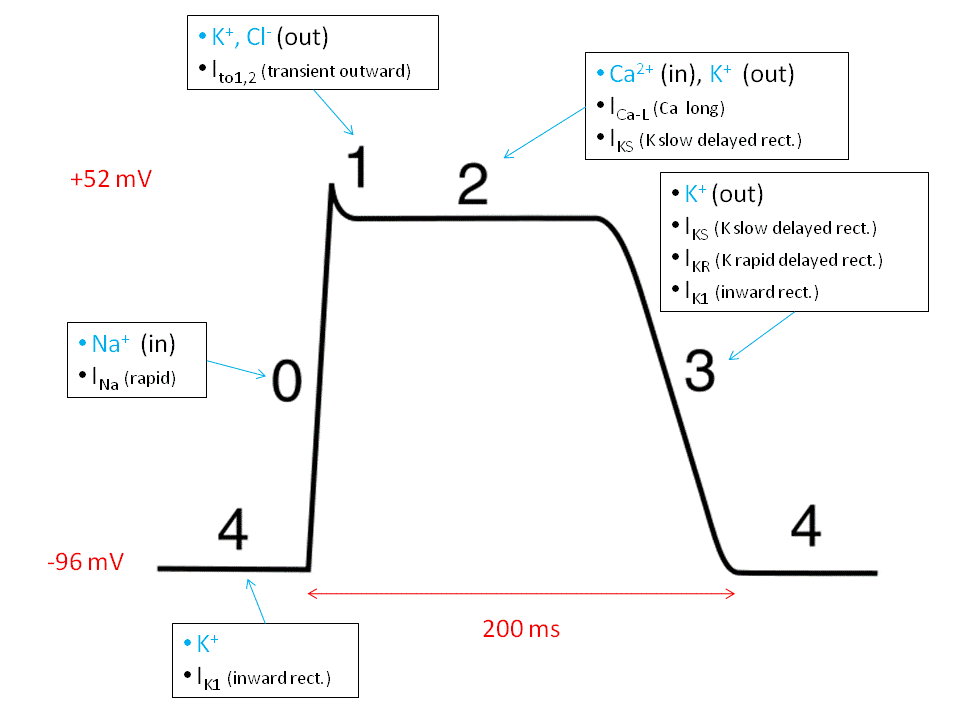
Splitting of S2 and Heart sounds. It has five distinct phases numbered 0-4. Like the autorhythmic cell it has protein transport channels but they are slightly different.
The Coordinated concentrations of the heart result from electrical changes that take place in cardiac cellsGas Transport System RespiratoryThe blood transpor. The particular action potential generated by cardiac pacemaker cells is very different to that in nerve and striated muscle cells and to that of ventricular myocardial cells. In the heart electrical impulses are generated by specialised pacemaker cells and spread across the myocardium in order to produce a coordinated contraction in systole.
That signals gotta start somewhere so some of these cells called pacemaker cells have the responsibility of setting the rhythm and the pace of. First the action potential of cardiac muscle is caused.
As elaborated in the chapter on the normal processes of cardiac excitation sodium is exchanged for calcium by the Na Ca 2 exchanger INCX during Phase 1 of the cardiac action potential.
The action potential generated is generated by a change in the potential difference between the. Cardiac output variables and equations. Pulmonary lungs systemic the rest of the body responsible for the flow of blood nutrients oxygen and other gases and hormones to and from cells about 2000 gallons 7572 liters of blood. Nervous and muscle cells as well as non-pacemaker cardiac cells use the opening of Na channels to facilitate the depolarisation phase whereas cardiac pacemaker cells. Learn the cardiovascular system. Cardiac action potential study guide by whitley_huie includes 13 questions covering vocabulary terms and more. We consider here the action potential of SA nodal cells and ventricular muscle cells. Cardiac cycle and the JVP waves. It is caused by a sudden increase in sodium inflow.
The basic function of the heart is to pump blood through the blood vessels. The cardiac action potential describes the molecular basis of electrical activity within the hearts cardiomyocytes. Pulmonary lungs systemic the rest of the body responsible for the flow of blood nutrients oxygen and other gases and hormones to and from cells about 2000 gallons 7572 liters of blood. Cardiac action potentials differ from the APs found in other areas of the body. Choose from 500 different sets of the cardiovascular system. Cardiac cycle and the JVP waves. Cells in the heart communicate this way.

































Post a Comment for "Cardiovascular System Cardiac Action Potential"